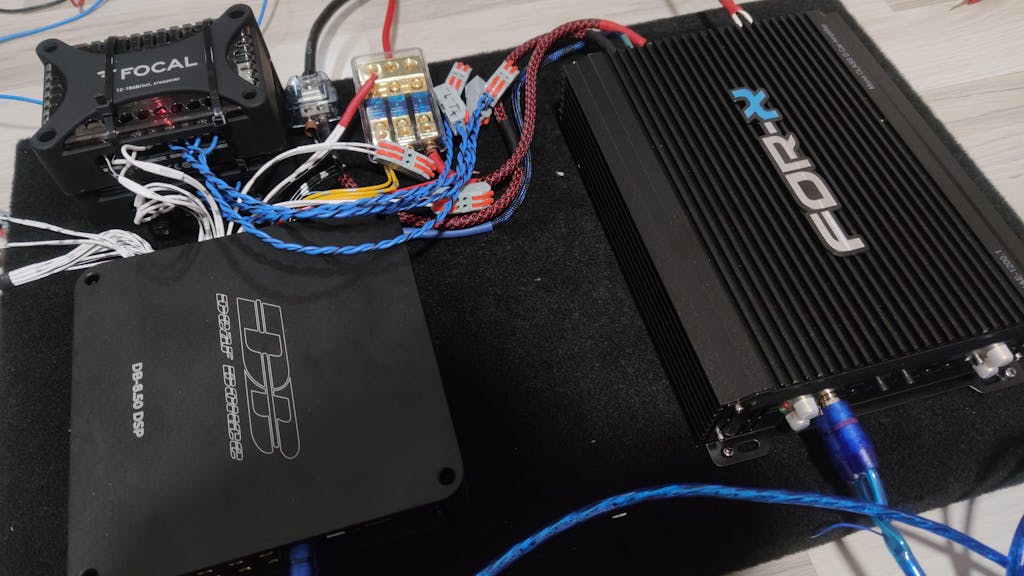
Vehicle Search
-
10mm²-20mm² Mini-ANL Splashproof

 Normal price €16,90Normal price
Normal price €16,90Normal price€16,90Selling price €16,905% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
4-600420 10mm²-50mm² Mini-ANL Splashproof

 Normal price €12,90Normal price
Normal price €12,90Normal price€12,90Selling price €12,905% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €29,00Normal price
Normal price €29,00Normal price€29,00Selling price €29,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 27, - Mar 4, -
 Normal price €59,00Normal price
Normal price €59,00Normal price€59,00Selling price €59,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
PG-3 35mm²-50mm² (mini)/ANL splash-proof

 Normal price €24,00Normal price
Normal price €24,00Normal price€24,00Selling price €24,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -
 Normal price €89,00Normal price
Normal price €89,00Normal price€89,00Selling price €89,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €25,00Normal price
Normal price €25,00Normal price€25,00Selling price €25,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €35,00Normal price
Normal price €35,00Normal price€35,00Selling price €35,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €39,00Normal price
Normal price €39,00Normal price€39,00Selling price €39,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 27, - Mar 4, -
 Normal price €69,00Normal price
Normal price €69,00Normal price€69,00Selling price €69,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €15,00Normal price
Normal price €15,00Normal price€15,00Selling price €15,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €9,00Normal price
Normal price €9,00Normal price€9,00Selling price €9,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price €29,00Normal price
Normal price €29,00Normal price€29,00Selling price €29,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price €29,00Normal price
Normal price €29,00Normal price€29,00Selling price €29,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 27, - Mar 4, -

 Normal price €15,00Normal price
Normal price €15,00Normal price€15,00Selling price €15,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €139,00Normal price
Normal price €139,00Normal price€139,00Selling price €139,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €19,00Normal price
Normal price €19,00Normal price€19,00Selling price €19,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €35,00Normal price
Normal price €35,00Normal price€35,00Selling price €35,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €109,00Normal price
Normal price €109,00Normal price€109,00Selling price €109,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €39,00Normal price
Normal price €39,00Normal price€39,00Selling price €39,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -
 Normal price €15,00Normal price
Normal price €15,00Normal price€15,00Selling price €15,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 27, - Mar 4, -

 Normal price €79,00Normal price
Normal price €79,00Normal price€79,00Selling price €79,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price From €55,00Normal price
Normal price From €55,00Normal price€55,00Selling price From €55,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €39,00Normal price
Normal price €39,00Normal price€39,00Selling price €39,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price From €69,00Normal price
Normal price From €69,00Normal price€69,00Selling price From €69,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price From €175,00Normal price
Normal price From €175,00Normal price€175,00Selling price From €175,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -

 Normal price €39,00Normal price
Normal price €39,00Normal price€39,00Selling price €39,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price €25,00Normal price
Normal price €25,00Normal price€25,00Selling price €25,005% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price €15,00Normal price
Normal price €15,00Normal price€15,00Selling price €15,005% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €19,90Normal price
Normal price €19,90Normal price€19,90Selling price €19,905% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26, -

 Normal price €14,90Normal price
Normal price €14,90Normal price€14,90Selling price €14,905% discount with prepaymentAvailable - Fast ShippingFeb 23, - Feb 24, -
 Normal price €9,95Normal price
Normal price €9,95Normal price€9,95Selling price €9,955% discount with prepaymentDelivery to HomeFeb 23, - Feb 26,
Wie wähle ich den richtigen Sicherungshalter für mein Audioprojekt aus?
Wie wähle ich den richtigen Sicherungshalter für mein Audioprojekt aus?
Was sind die Vor- und Nachteile von Sicherungshaltern mit LED-Anzeige?
Was sind die Vor- und Nachteile von Sicherungshaltern mit LED-Anzeige?
Wie installiere ich Sicherungshalter richtig, um maximale Performance zu gewährleisten?
Wie installiere ich Sicherungshalter richtig, um maximale Performance zu gewährleisten?
Warum sind Sicherungshalter essentiell für den Schutz meiner Carhifi Anlage?
Warum sind Sicherungshalter essentiell für den Schutz meiner Carhifi Anlage?
Welche Rolle spielen Materialien bei der Auswahl eines Sicherungshalters?
Welche Rolle spielen Materialien bei der Auswahl eines Sicherungshalters?
Wie integriere ich Sicherungshalter effizient in bestehende Carhifi-Systeme?
Wie integriere ich Sicherungshalter effizient in bestehende Carhifi-Systeme?
Wie kann ich die Leistung meiner Carhifi-Anlage mit Sicherungshaltern optimieren?
Wie kann ich die Leistung meiner Carhifi-Anlage mit Sicherungshaltern optimieren?
Was muss ich bei der Auswahl von Mehrfachsicherungshaltern beachten?
Was muss ich bei der Auswahl von Mehrfachsicherungshaltern beachten?
Worauf sollte ich bei der Montage von Sicherungshaltern in unterschiedlichen Fahrzeugen achten?
Worauf sollte ich bei der Montage von Sicherungshaltern in unterschiedlichen Fahrzeugen achten?
Wie beeinflussen Sicherungshalter die Klangqualität meines Audiosystems?
Wie beeinflussen Sicherungshalter die Klangqualität meines Audiosystems?